Spaghetti Models: Spaghetti Models For Beryl
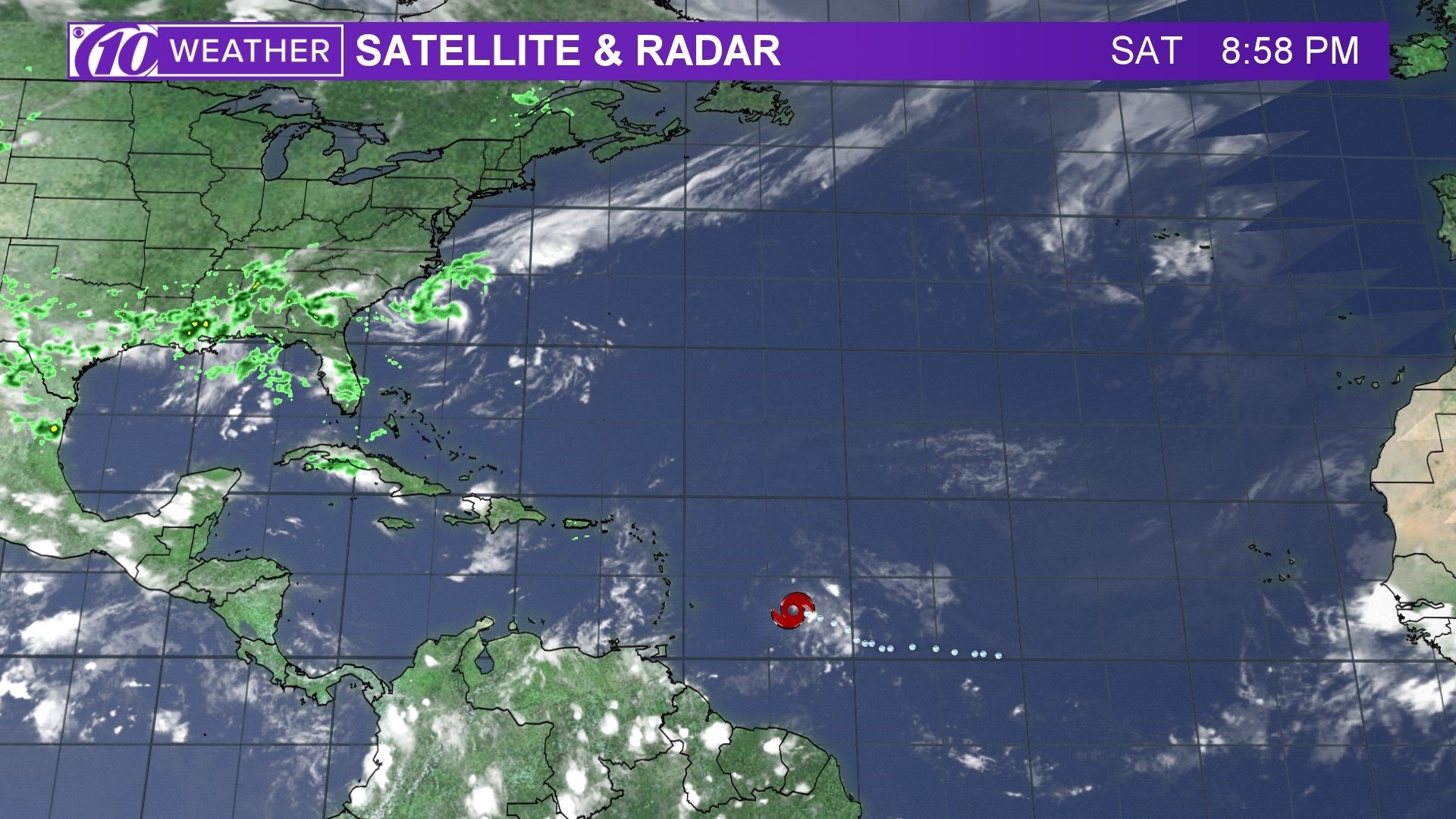
Spaghetti models for beryl – Spaghetti models, a type of ensemble forecasting technique, have been employed in weather prediction for decades. Their origins can be traced back to the early 20th century when meteorologists recognized the inherent uncertainties in weather forecasting and sought methods to account for these uncertainties.
In the 1960s, Edward Lorenz, a pioneer in chaos theory, demonstrated the sensitive dependence of weather forecasts on initial conditions. This concept, known as the butterfly effect, highlighted the need for probabilistic forecasting methods that could capture the range of possible outcomes.
The development of spaghetti models gained momentum in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of powerful computers and the emergence of ensemble forecasting techniques. Ensemble forecasting involves running multiple model simulations with slightly different initial conditions or model configurations. The spread of these individual model runs provides an indication of the uncertainty in the forecast.
Key Figures and Institutions
- Edward Lorenz (Massachusetts Institute of Technology): Pioneer in chaos theory and the butterfly effect.
- National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR): A leading institution in the development and application of spaghetti models.
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): A major center for ensemble forecasting and the production of spaghetti models.
Scientific Principles, Spaghetti models for beryl
Spaghetti models are based on the principle of ensemble forecasting. By running multiple model simulations with slightly different initial conditions or model configurations, meteorologists can capture the range of possible weather outcomes.
The spread of the individual model runs provides an indication of the uncertainty in the forecast. A narrow spread suggests that the forecast is more certain, while a wider spread indicates greater uncertainty.
Spaghetti models have been refined over time to improve their accuracy and reliability. Advances in computer technology have allowed for higher-resolution models and more ensemble members, leading to more detailed and precise forecasts.
Applications of Spaghetti Models in Beryl Analysis

Spaghetti models have gained significant traction in the analysis of beryl, a gemstone mineral, due to their ability to provide valuable insights into the spatial distribution and geological characteristics of beryl deposits. These models have proven particularly useful in various applications, including mineral exploration, resource assessment, and geostatistical modeling.
Mineral Exploration
Spaghetti models have been successfully employed in mineral exploration to identify potential beryl-bearing zones and prioritize exploration targets. By analyzing the spatial relationships between beryl occurrences and geological features, these models can help geologists delineate areas with higher probabilities of beryl mineralization. This information can guide exploration efforts, reducing the time and resources required to locate viable beryl deposits.
Resource Assessment
Spaghetti models are also valuable tools for resource assessment, providing estimates of the quantity and quality of beryl resources. By simulating the distribution of beryl within a deposit, these models can help geologists determine the economic viability of mining operations. This information is crucial for decision-making related to mine planning and development.
Geostatistical Modeling
Spaghetti models have been integrated with geostatistical techniques to create more sophisticated models of beryl deposits. These models incorporate statistical methods to quantify the spatial variability of beryl and estimate its grade and tonnage. Geostatistical spaghetti models provide a comprehensive understanding of the deposit’s characteristics, enabling geologists to make informed decisions regarding mining strategies and resource management.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the successful application of spaghetti models in beryl analysis. For example, in the pegmatites of Madagascar, spaghetti models were used to identify zones with high beryl concentrations, leading to the discovery of several new beryl-bearing pegmatites. In Brazil, spaghetti models were employed to assess the resource potential of a large beryl deposit, providing valuable information for mine planning and development.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their advantages, spaghetti models have certain limitations and challenges in beryl analysis. These models rely on accurate geological data, which may not always be available or reliable. Additionally, the complexity of beryl deposits and the influence of multiple geological factors can make it challenging to create accurate spaghetti models. Nevertheless, with careful data analysis and validation, spaghetti models can provide valuable insights into beryl deposits, aiding in exploration, resource assessment, and geostatistical modeling.
Spaghetti models for Beryl show various paths it could take, with some indicating a potential landfall. To stay informed about Beryl’s trajectory, visit where is beryl headed. This site provides up-to-date information on Beryl’s location and projected path, helping you make informed decisions about your safety.
Spaghetti models for Beryl show a range of possible paths the storm could take. To stay up-to-date on the latest projections, check the beryl projected path. The spaghetti models will continue to be updated as new data becomes available, so it’s important to stay informed about the storm’s potential impact.